On 1st December 2022 Government of India & Reserve Bank of India introduced Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), a digital form of currency notes like cryptocurrency but not decentralized, on pilot bases in 4 cities in the country as a future currency & payment system. CBDC is a fiat currency which means it is not backed by Gold & Silver albeit consider a form of legal tender that can be used in transactions and exchanges of goods. Currently, more than 100 central banks all across the globe have trodden in this conduit so, here the question is, can India’s CBDC supersede the Global payment method SWIFT? Let’s see a glimpse of this payment system.
What is SWIFT?
SWIFT stands for Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, founded in 1973 with 239 banks in 15 countries, a global payment system (Cross border transaction) came into the limelight during the ongoing Russia- Ukraine war when western countries demanded a moratorium to Russia from the SWIFT payment system to give him economic thwack. SWIFT is operational in more than 11,000 financial Institutions and companies across the world in over 200 countries. SWIFT has gained trust as the most dominant and standardized method for sending money to receipts across the border safely, securely, and relatively quickly.
How does it work?
SWIFT works as messaging network that is used by financial institutions to securely transmit information and instruction through a standardized system of codes. Swift does not transfer or hold assets rather it facilitates secure and efficient communication between two institutions. A unique BIC (Bank identifier code) code is used in a transaction which is having eight to eleven characters in alphanumeric form.
For example, a Bank ABC customer wants to send money to a friend in the USA, who has an account with Bank XYZ, The ABC customer can do this by entering the details of the XYZ customer i.e., his account number, bank code, country code & SWIFT code. Once this transaction happened ABC will send a SWIFT message to XYZ, and after getting verified by XYZ the recipient will get the credit in their account.
Why CBDC e₹?
Here, we will see the scope of digital currency in two ways: one in India and the other at the global level. According to reports, RBI has spent nearly Rs. 5,000 crores in 2021-22 on printing of currency, Rs.4012.09 crores in the year 2020-21, and nearly Rs. 8000 crores during demonetization, so by introducing Digital currency, RBI can reduce the cost of printing of physical currency and another cascading cost.
| Denomination | Price Per Thousand pieces (in Rs) | Price per Note (in Rs) |
| Rs 10 | 1010 | 1.01 |
| Rs 20 | 1000 | 1 |
| Rs 50 | 1010 | 1.01 |
| Rs 100 | 1510 | 1.51 |
| Rs 500 | 2570 | 2.57 |
| Rs 2000 | 4180 | 4.18 |
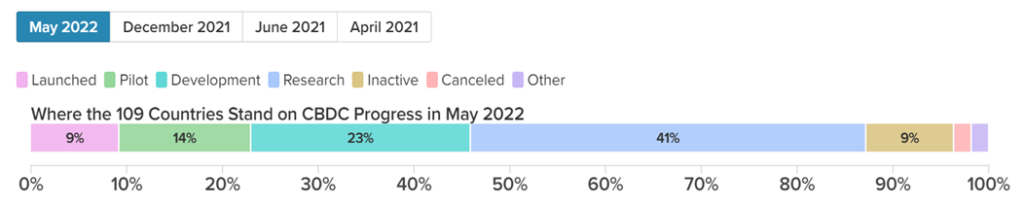
The second one is that the world has a robust, fast, and cost-effective payment method for clothing ss-border transactions at breakneck speed, the central bank of many nations like Germany, China, the USA, and many European countries are trying to decode the digital currency maze. For the Bank of Canada launch project Jasper, UAE, and Saudi Arabia launch bilateral project Aber, etc.
Timeline: Race for Future Money
Payment system like SWIFT takes a minimum of 3 to 4 days to reflect the amount in the beneficiary account also bank charges 3% to 5% for exchanging money through swift, on another hand CBDC arrangement for a faster, cheaper, and more efficient mechanism for transfers and foreign exchange operations. If we succeeded in this & our digital currency is accepted at the global level, then India will snatch the dominance of western countries in the global money transfer system.
Source: Atlantic.org/RBI Annual report/ Businessline/outlookindia.com




