The Union Budget 2025-26 was presented in Parliament by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, emphasizing four engines of development: Agriculture, Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), Investment, and Exports. With the overarching theme of ‘Sabka Vikas’, the budget aims to promote balanced growth across all regions while laying out the broad principles of ‘Viksit Bharat’—a vision of an economically advanced and inclusive India.
Key Focus Areas of Budget 2025-26
The finance minister has structured the budget around supporting four key segments of society:
- The Poor (Garib)
- Youth (Yuva)
- Farmers (Annadata)
- Women (Nari)
This year’s budget introduces bold reforms, higher spending on rural development, infrastructure expansion, and investment-friendly policies. Below is a sector-wise breakdown of the major initiatives under the four engines of development:
The Four Engines of Development
1st Engine- Agriculture: Strengthening the Backbone of the Economy
- Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana: A new initiative covering 100 low-productivity agricultural districts, benefiting 1.7 crore farmers with improved irrigation and post-harvest storage facilities.
- Rural Prosperity and Resilience Program: A collaborative effort with states to reduce agricultural underemployment through skilling, investment, and technology adoption.
- Atmanirbharta in Pulses: A 6-year mission focusing on Tur, Urad, and Masoor pulses, ensuring climate-resilient seeds and remunerative pricing mechanisms.
- MSP Support for Farmers: Government agencies NAFED and NCCF will be ready to procure pulses over the next four years to stabilize prices and support farmers.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Loan Limit: Increased from ₹3 lakh to ₹5 lakh, benefiting 7.7 crore farmers with enhanced access to agricultural credit.
- National Mission on High Yielding Seeds: A research-driven initiative to improve availability of over 100 high-yielding, pest-resistant seed varieties.
- Mission for Cotton Productivity: A five-year program promoting sustainable farming and boosting the production of extra-long staple cotton.
- Makhana Board in Bihar: A dedicated board for improving the production, processing, and value addition of Makhana, enhancing incomes for farmers in Bihar.
- Fisheries Development: A new framework for sustainable fishing in India’s Exclusive Economic Zone and High Seas, with a special focus on Andaman, Nicobar, and Lakshadweep.
- Urea Plant in Assam: A 12.7 lakh metric ton capacity plant under Brahmaputra Valley Fertilizer Corporation Ltd to boost domestic fertilizer production.
2nd Engine- MSMEs: Expanding Credit and Market Opportunities
Revised MSME Classification: Investment and turnover limits raised by 2.5 times, enabling better access to finance and promoting business expansion.

- Micro Enterprise Credit Cards: A ₹5 lakh credit facility for 10 lakh micro enterprises, promoting financial inclusion.
- MSME Credit Guarantee Expansion: Guarantee cover increased from ₹5 crore to ₹10 crore, enabling small businesses to secure higher loans.
- Focus Product Scheme for Leather and Footwear: Projected to generate 22 lakh jobs, with an expected turnover of ₹4 lakh crore and ₹1.1 lakh crore in exports.
- Toy Industry Development: Formation of clusters and R&D initiatives to promote ‘Made in India’ toys for global markets.
- National Institute of Food Technology: A new food technology, entrepreneurship, and management institute in Bihar to boost food processing and agri-business.
- Fund of Funds for Startups: Expansion of the startup ecosystem with an additional ₹10,000 crore fund for innovation and business development.
3rd Engine- Investment: Driving Infrastructure and Innovation
- Urban Challenge Fund: ₹1 lakh crore allocated for ‘Cities as Growth Hubs,’ creative redevelopment, and water & sanitation projects.
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Funding increased to ₹67,000 crore, extending the initiative to 2028 to achieve universal piped water connectivity.
- Maritime Development Fund: ₹25,000 crore fund for shipbuilding, ports, and logistics, with 49% government contribution.
- IIT Expansion: 6,500 additional student seats across five newly established IITs, strengthening India’s higher education sector.
- PM Research Fellowship: 10,000 research fellowships for advanced studies in IITs and IISc.
- Healthcare Expansion: 200 new Day Care Cancer Centers will be set up in 2025-26, ensuring affordable and accessible cancer treatment.
- Nuclear Energy Mission: A ₹20,000 crore fund dedicated to Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) with a plan to operationalize five reactors by 2033.
- UDAN Scheme for Regional Connectivity: Strengthening air connectivity by linking 120 new destinations and supporting regional airports and helipads.
- Greenfield Airport in Bihar: Development of new airports in Bihar to improve regional connectivity.
4th Engine- Export Promotion: Strengthening Global Trade Competitiveness
- Export Promotion Mission: A sector-focused strategy to boost exports, led by the Ministries of Commerce, MSME, and Finance.
- Bharat Trade Net (BTN): A unified digital trade platform facilitating international trade documentation and financing solutions.
- Global Capability Centres (GCCs): Incentivizing Tier-2 cities to become outsourcing hubs for multinational corporations.
- Warehousing for Air Cargo: Expansion of storage and processing infrastructure for high-value perishable exports.
Taxation and Financial Reforms
Income Tax Reforms: No income tax for individuals earning up to ₹12 lakh per annum (₹12.75 lakh for salaried employees with deductions).
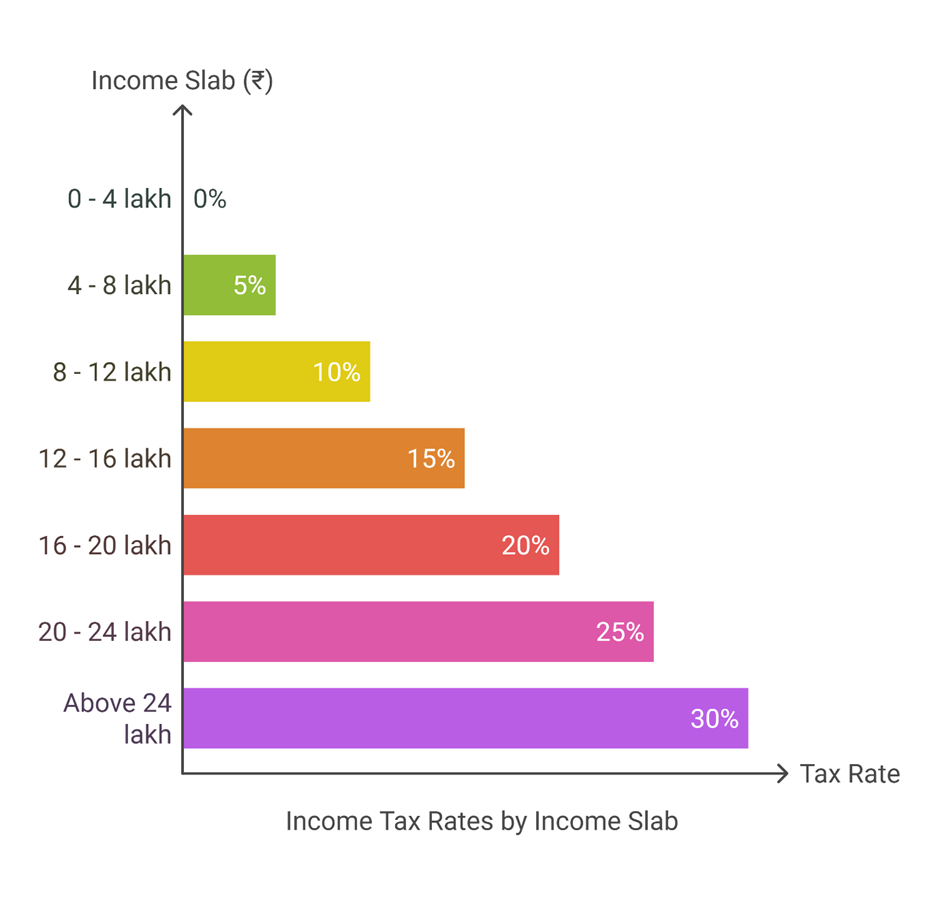
- TDS on Rent: Threshold increased from ₹2.4 lakh to ₹6 lakh, reducing compliance burdens.
- Basic Customs Duty (BCD) Exemptions: 36 life-saving drugs, lithium-ion battery components, and textile/electronic parts fully exempted to boost domestic production.
Social Welfare and Inclusion
- PM SVANidhi Scheme: UPI-linked credit cards with ₹30,000 limit for street vendors.
- Identity Cards for Gig Workers: Registration on the e-Shram portal ensuring social security.
- 50,000 Atal Tinkering Labs: To promote innovation in schools over five years.
- Medical Education: 10,000 new medical seats, aiming for 75,000 seats in five years.
Financial Sector Reforms
- Grameen Credit Score: Enabling SHG members better access to formal credit.
- Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0: Decriminalizing 100+ legal provisions to ease business.
- SWAMIH Fund 2.0: ₹15,000 crore fund for completing 1 lakh dwelling units.
- FDI in Insurance: Increased from 74% to 100% for firms investing premiums in India.
- Investment Friendliness Index: A new ranking framework for states.
- Pension Sector Reforms: New forum for regulatory coordination and pension products.
Major Sources of Revenue and Expenditure from the Budget:
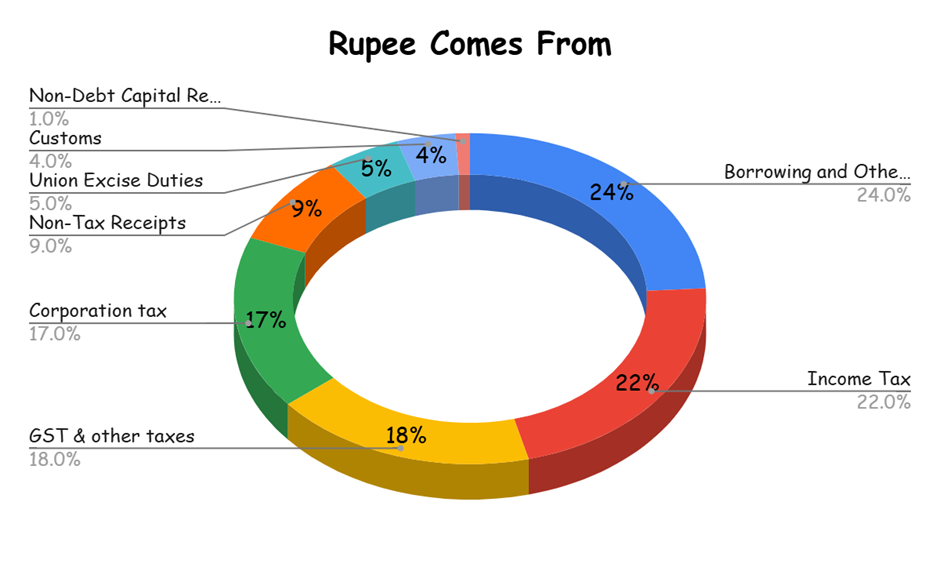
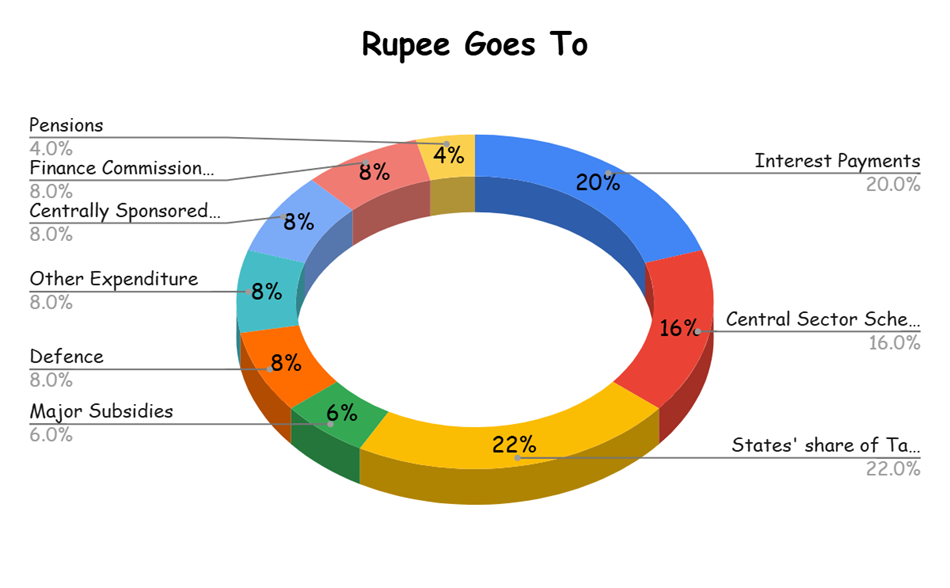
Major Central Govt Expenditure (Budget Estimates):
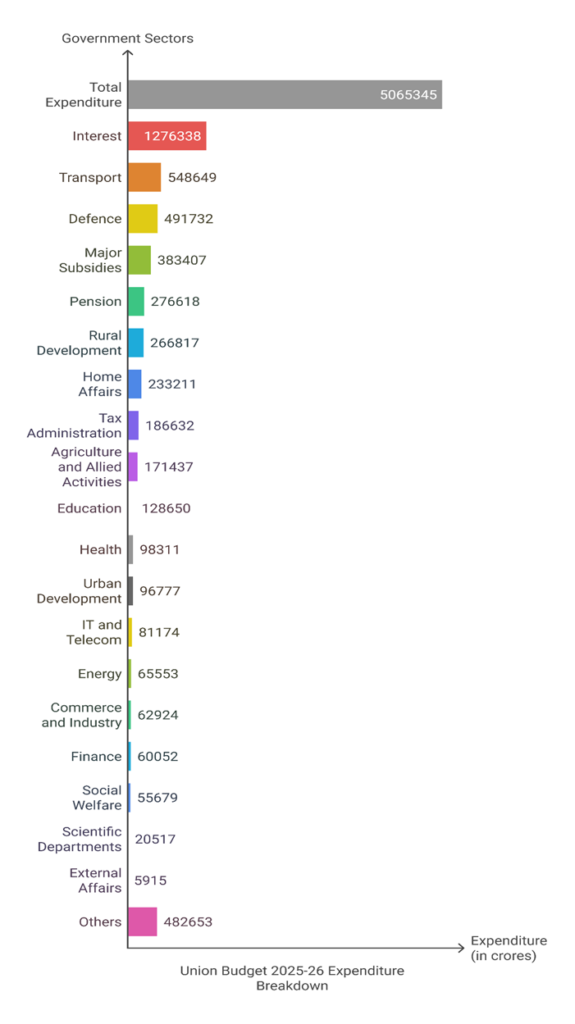
Key Numbers:
| Metric (In Rs crore) | 2023-24 (Actuals) | 2024-25 (Budget Estimates) | 2024-25 (Revised Estimates) | 2025-26 (Budget Estimates) |
| Revenue Receipts | 27,29,036 | 31,29,200 | 30,87,960 | 34,20,409 |
| Capital Receipts | 17,14,411 | 16,91,312 | 16,28,527 | 16,44,936 |
| Total Receipts | 44,43,447 | 48,20,512 | 47,16,487 | 50,65,345 |
| Total Expenditure | 44,43,447 | 48,20,512 | 47,16,487 | 50,65,345 |
| Effective Capital Expenditure | 12,53,111 | 15,01,889 | 13,18,320 | 15,48,282 |
| Revenue Deficit | 7,65,216 | 5,80,201 | 6,10,098 | 5,23,846 |
| Effective Revenue Deficit | 4,61,300 | 1,89,423 | 3,10,207 | 96,654 |
| Fiscal Deficit | 16,54,643 | 16,13,312 | 15,69,527 | 15,68,936 |
| Primary Deficit | 5,90,771 | 4,50,372 | 4,31,587 | 2,92,598 |
The Union Budget 2025-26 presents a strategic and growth-oriented vision for India, addressing economic development, rural empowerment, and financial resilience. By focusing on agriculture, MSMEs, infrastructure, and exports, the budget aims to drive inclusive and sustainable growth. Increased allocations for farmer support, MSME credit access, and digital trade platforms reflect a strong commitment to boosting rural and industrial productivity. However, effective implementation and monitoring will be key to ensuring these policies translate into real economic impact. Continued focus on climate resilience in agriculture, infrastructure expansion, and financial inclusion will shape India’s long-term growth trajectory, making it a more self-reliant and globally competitive economy.
Sources
https://www.ibef.org/download/Union-Budget-2025-26-Speech.pdf
https://www.ibef.org/download/Union-Budget-2025-26-Annual-Financial-Statement.pdf
https://www.ibef.org/download/Union-Budget-2025-26-Key-Features.pdf




