As the world grapples with the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change, India’s railway system is making a bold move to contribute to a greener future. Indian Railways, one of the largest and busiest rail networks in the world, has set an ambitious target of becoming a net zero carbon emitter by 2030. A key component of this effort is the introduction of hydrogen-powered trains, an innovation that promises to revolutionize rail transport while significantly reducing pollution. With this development, India will join Germany, France, Sweden and China.
Image- Countries with existing FCH (fuel cum hydrogen trains)
source- https://rail-research.europa.eu/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Report-1.pdf
The Hydrogen Train Initiative
Hydrogen-powered trains, commonly referred to as “hydrail,” use hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, emitting only water vapor and heat as by-products. This makes them a highly attractive option for reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions in the transportation sector. Indian Railways is planning to roll out these green trains as part of its broader goal of achieving net-zero emissions by the end of the decade.
The first hydrogen train in India is expected to begin operation in the 2024-25 financial year, following an initial testing phase will start in Dec 2024. The trial runs will take place on the 89-kilometer Jind-Sonipat section of the Delhi division. This pilot project is an important first step, not only for testing the feasibility of hydrogen trains in India but also for showcasing how clean technology can transform the country’s rail infrastructure.
Expanding Hydrogen Train Networks
The initial hydrogen train project is just the beginning of a more ambitious plan. Indian Railways aims to deploy 35 hydrogen-powered trains across various heritage and hilly routes, which have historically been difficult to electrify due to geographical and logistical challenges. This project has been named Hydrogen for Heritage, and it underscores the potential of hydrogen-powered trains to serve as a sustainable alternative to traditional diesel-powered locomotives in remote and ecologically sensitive areas.
Hydrogen trains offer several environmental benefits. Unlike diesel trains, which emit harmful pollutants and greenhouse gases, hydrogen trains produce zero direct emissions. They are powered by fuel cells that generate electricity by combining hydrogen with oxygen, with water being the only waste product. The adoption of hydrogen trains will significantly reduce India’s carbon footprint and align the country’s railway sector with global sustainability goals.
Financial Investments in Green Transportation
To support the transition to hydrogen-powered trains, Indian Railways has allocated a substantial budget. In the 2024 Union Budget, a provision of Rs 2,800 crore was set aside for the purchase and deployment of 35 hydrogen trains. In addition, Rs 600 crore has been earmarked for building the necessary infrastructure to support hydrogen fuel technology, especially on heritage routes where traditional electrification is not feasible.
These investments reflect the government’s commitment to making India’s railway network more sustainable and energy-efficient. Furthermore, the Indian Railways is working on a project to convert a diesel-powered DEMU (Diesel Electric Multiple Unit) train into a hydrogen-powered vehicle. This retrofit initiative, with a contract value of Rs 111.83 crore, will involve installing hydrogen fuel cells in the train and building the requisite infrastructure on the ground to support this transformation.
A Multidimensional Approach to Sustainability
The hydrogen train initiative is just one part of Indian Railways’ broader strategy to reduce its carbon footprint and increase energy efficiency. The Railways is also adopting Head on Generation (HOG) technology to save power, installing LED lights in trains and stations, and replacing older, less efficient equipment with energy-saving alternatives. Additionally, Indian Railways is planting trees along tracks and developing solar power plants at stations and across railway land to further reduce its environmental impact.
These initiatives demonstrate Indian Railways’ holistic approach to achieving sustainability. By embracing a combination of renewable energy sources, modern energy-efficient technologies, and green infrastructure, the railways is setting a precedent for other sectors in India to follow.
Hydrogen as the Future of Green Transportation
The move to hydrogen trains is part of India’s broader efforts to transition to green transportation. Hydrogen, as a clean fuel, holds immense potential for reducing dependence on fossil fuels and cutting emissions from transportation, which is a major contributor to air pollution and climate change. By producing hydrogen using renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power, India can reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and create a self-sustaining, low-emission transportation ecosystem.
The hydrogen train project is also expected to have a ripple effect on other sectors of the economy. By developing hydrogen infrastructure, India could become a global leader in the emerging hydrogen economy, creating new jobs, driving innovation, and attracting investment in clean energy technologies. Moreover, the successful deployment of hydrogen-powered trains could pave the way for their adoption in other forms of transport, such as buses and trucks, contributing to a nationwide shift toward sustainable mobility.
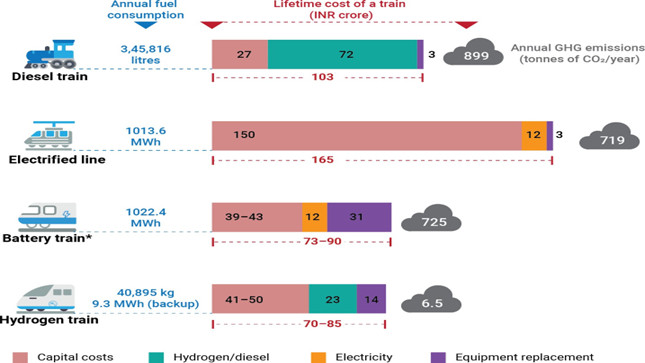
| Study of a Hydrogen Train on Shimla-Kalka Route https://cstep.in/drupal/sites/default/files/2023-07/Potential%20and%20Challenges%20of%20Using%20Hdrogen%20to%20Decarbonise% 20Indian%20Railways.pdf |
Conclusion
The launch of hydrogen-powered trains by Indian Railways marks a significant step in India’s journey toward a greener, more sustainable future. With an investment of Rs 2,800 crore and plans to deploy 35 hydrogen trains, the railway is taking decisive action to reduce its carbon footprint and help India achieve its net-zero emissions target by 2030. This project aligns with global trends in clean transportation and positions India as a forward-thinking leader in the green mobility revolution.
As the first hydrogen-powered trains prepare to roll out, they will serve not only as a symbol of India’s commitment to climate action but also as a practical solution to some of the most pressing environmental challenges facing the country. By embracing hydrogen technology, Indian Railways is proving that sustainable transportation can be both environmentally responsible and economically viable, paving the way for a cleaner, more efficient future for India’s rail network and beyond.




